Our Mission
To advance Philippine ICT industries by delivering innovative Nework Test, Monitoring systems and Cybersecurity solutions based on global standards and best practices that drive our customer’s business to new levels.
Our Vision
Testronix aims to be the premier brand in the Philippines for ICT Network Test, Cybersecurity solutions and Monitoring systems. We envision our company as symbol of product reliability, customer value and service excellence.
Comprehensive Guide to Telecom Testing
(Including Tools, Test CasesA , and Best Practices)
We live in an increasingly connected world, a reality made possible by the vital advancements of the telecommunications industry. With 5G technology becoming widespread, the rapid growth of IoT, and the rising influence of AI, the telecom sector is poised for an exciting future. However, this rapid growth necessitates ongoing, thorough telecom testing to ensure consistent service quality at the highest standards.
In this article, we’ll dive into the importance of telecom testing, the common challenges and pitfalls faced, and the best practices to follow in this field.

What is Telecom Testing?
Telecom testing involves evaluating telecommunications systems, services, and networks to ensure they function properly, perform efficiently, and remain reliable. The goal of telecom testing is to uphold and improve the user experience while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Telecom testing is particularly complex due to the diverse technologies involved, such as voice, data, and multimedia services, each with its own protocols that can interact with and impact one another. As digital transformation accelerates and user expectations rise, QA teams are challenged to deliver quality at an ever-increasing pace, making effective telecom testing a significant achievement.
Benefits of Telecom Testing
Improved User Experience:
As customer expectations continue to rise in the telecom industry, providers are expected to offer personalized experiences, seamless omnichannel services, and rapid issue resolution. In this complex landscape, conducting thorough, strategic testing is essential for identifying areas of optimization and improvement, ultimately enhancing the user experience.
Reliable Services:
Telecom services must remain consistently available and accurate, particularly in critical situations and emergencies where dependable communication can be a matter of life or death.
Network Resource Optimization:
Serving millions of users daily, telecom companies must make data-driven decisions to allocate resources efficiently and deliver high-speed services. Performance testing helps identify optimal strategies and plan for unexpected surges in demand.
Data Security and Privacy:
As an industry reliant on data transmission, telecom companies face significant concerns around data security and privacy. With the constant threat of cyberattacks and data breaches, industry leaders must stay vigilant, continuously testing encryption protocols, authentication systems, and other protective measures.
Adoption of Emerging Technologies:
The introduction of new technologies like 5G, IoT, and AI-powered services is set to revolutionize digital applications and services. While exciting, these innovations also present novel challenges. Rapid progress must not come at the cost of quality, and thorough testing will ensure the telecom industry remains resilient in the face of change.
Regulatory Compliance:
Given the vast amount of sensitive data managed by telecom networks, companies must consistently demonstrate adherence to industry standards. Testing ensures that system designs comply with regulatory requirements and best practices.
Understanding the Telecom Domain in Testing
- Easier design and execution of a test strategy specific to telecommunication services and technologies, ensuring all critical areas are covered.
- The ability to more accurately simulate real-life telecom scenarios.
- Early identification of potential issues and risks.
- Simplified exploratory testing, where testers proactively explore the telecom system without predefined test cases to uncover hidden bugs.
- Improved communication between testing teams, developers, and other stakeholders, thanks to a shared understanding of telecom terminology.
- Increased overall productivity.
- Reduced need for training due to familiarity with telecom business processes.
- Cellular Networks (3G, 4G, 5G)
- Voice over IP (VoIP)
- Fiber Optics
- Roaming and Handover
- Signal Propagation
- Network Topologies
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Network Security
- Spectrum Allocation
- Broadband Technologies
- Call Routing
- Data Compression
- Telecommunications Standards
- Mobile Apps and Services
- Network Virtualization
- Satellite Communication
- Billing and Charging Systems

Business Processes in the Telecom Industry
In simple terms, telecommunications enable individuals and businesses to communicate and share information globally. It serves as the backbone of the digital economy, ensuring seamless connections between people and organizations. Key activities and processes in the telecom industry include:
Network Infrastructure Development:
- Builds the physical foundation of networks for reliable communication.
- Facilitates global data transmission, connecting individuals and devices.
- Lays the groundwork for the implementation of advanced technologies and services.
Telecom Services Provisioning:
- Enables communication, collaboration, and access to information.
- Addresses a wide range of communication needs, from voice calls to multimedia content.
- Supports economic growth by linking businesses and individuals.
Network Management:
- Ensures optimal network performance and minimizes service interruptions.
- Maintains service quality for a positive user experience.
- Improves network efficiency and reliability through continuous monitoring and optimization.
Network Operations:
- Monitors network health and resolves issues promptly.
- Keeps communication channels open and functioning smoothly.
- Prevents downtime and ensures continuous service availability.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- Builds trust by resolving customer queries and issues.
- Strengthens customer loyalty through positive experiences.
- Enhances customer satisfaction and boosts brand reputation.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensures adherence to legal standards, avoiding penalties and operational disruptions.
- Safeguards customer data privacy and upholds industry credibility.
- Creates a framework for fair competition and sustainable industry growth.
Service Differentiation and Innovation:
- Differentiates businesses with unique offerings and features.
- Meets evolving customer needs, enhancing loyalty.
- Drives revenue growth by attracting new customers and retaining existing ones.
Billing Management:
- Ensures accurate billing, preventing disputes and customer dissatisfaction.
- Facilitates efficient revenue collection to sustain operations.
- Supports transparency in financial dealings between customers and providers.
Emergency Services:
- Saves lives by enabling timely access to emergency support.
- Provides accurate location data for effective emergency responses.
- Enhances public safety and overall societal well-being.
Network Expansion:
- Extends coverage to underserved areas, reducing the digital divide.
- Supports the increasing demand for communication in a connected world.
- Accommodates the growing need for data and services.
Research and Development (R&D):
- Fosters innovation and keeps the telecom industry competitive.
- Drives technological advancements that benefit both users and businesses.
- Supports the development of new services and solutions.
Each of these critical processes relies on robust testing to maintain their quality. For example, in network infrastructure development, testing ensures the proper installation and optimization of physical network components. For telecom service provisioning, QA teams focus on user-centric testing to ensure seamless service access and uninterrupted user experience.
OSS and BSS in Telecommunications
The core activities in telecommunications can be broadly classified into two main categories:
- OSS (Operations Support System): Software, devices, and applications designed to manage the technical operations of a telecommunications network.
- BSS (Business Support System): Systems designed to support the business side of telecom services, including billing, customer relationship management (CRM), service delivery, and more.

While OSS and BSS address different functions within a telecom organization, they often work together to enhance the full range of telecom services.
Both OSS and BSS take advantage of cloud computing, automation tools, and data analytics to streamline processes across the entire telecom operation, from internal functions to customer interactions. The integration of these systems allows telecom providers to seamlessly connect customers with reliable technology solutions.
Given the close relationship between customer issues and network performance, it makes sense for these two systems to collaborate. By working in tandem, OSS and BSS help telecom companies overcome industry challenges, maintain reliable network services, and improve the overall customer experience. This integrated approach fosters innovation, resilience, and higher customer satisfaction across the telecom industry.
A typical workflow in the telecom industry generally follows these steps:
- Conduct market research to understand customer needs.
- Design the network architecture based on research insights.
- Perform capacity planning to ensure the network can handle projected traffic.
- Install and configure the physical network infrastructure (e.g., switches, routers, base stations).
- Establish communication links between network touchpoints.
- Conduct functional testing to ensure the system meets expected features.
- Activate services based on customer requests.
- Capture customer information and create their profiles in the CRM system.
- Monitor performance metrics to maintain service quality.
- Rate usage according to service plans, tariff structures, and pricing policies.
- Generate invoices and bills for customers with itemized usage details.
- Address customer inquiries, complaints, and technical issues through support channels.
- Identify and resolve potential issues and bottlenecks.
- Research and develop new telecom services and features to stay competitive.
Testing Life Cycle in the Telecom Industry
- Requirement Analysis
- Test Planning
- Test Case Development
- Environment Setup
- Test Execution
- Test Cycle Closure
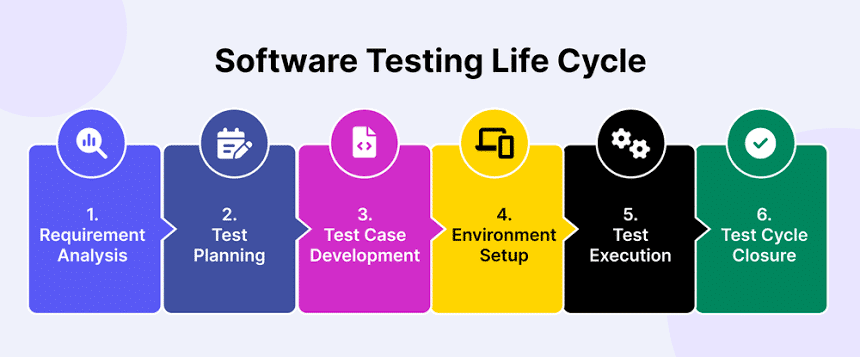
During the Requirement Analysis phase, testers and key stakeholders come together to define the project’s objectives. This involves three parties: the Product Owner, the Developer, and the Tester, each bringing a unique perspective. The communication gap between their distinct approaches, often due to differences in the “language” they use, highlights the need for Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) testing. BDD allows the creation of user stories and scenarios in business-readable terms rather than technical jargon, ensuring all parties involved can easily understand the goals.
Once the requirements are established, testers create a comprehensive test plan that outlines the necessary test cases and the specific environment configurations required for effective execution. The test execution is then scheduled, and the results are analyzed in detail to gather insights for decision-making and future improvements.
Examples of Telecom Test Cases
| Test Case | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Call Connectivity Test | Verify that calls are successfully established and that the call quality meets expectations between two numbers. |
| SMS Functionality Test | Test the sending and receiving of SMS messages, ensuring the content and order are accurate. |
| Data Connection Test | Access various websites and verify consistent data speeds across different network types. |
| Roaming Functionality Test | Test seamless network switching between home and roaming networks, ensuring uninterrupted service. |
| Voicemail Functionality Test | Test the ability to leave, save, and retrieve voicemail messages accurately. |
| Call Waiting Test | Test the call waiting feature by holding one call and answering another, ensuring smooth transitions. |
| Conference Call Test | Test the creation and participation in multi-participant conference calls with clear communication. |
| Call Forwarding Test | Test call forwarding settings, including enabling, disabling, and modifying them as needed. |
| Network Coverage Test | Test signal strength in various locations (urban, rural, indoor, outdoor) to assess reliability. |
| Emergency Call Test | Test the ability to make emergency calls, even with limited network coverage, ensuring successful connections. |
| Balance and Usage Test | Test the accuracy of account balance and usage details. |
| International Roaming Test | Test service functionality and verify charges when using telecom services abroad. |
| Call Drops and Handover Test | Test the seamless handover of calls between cell towers, ensuring no call drops. |
| Network Switch Test | Test the device’s ability to switch between different network technologies based on availability. |
| Network Compatibility Test | Test the device’s compatibility with various network bands and frequencies. |
| SIM Card Functionality Test | Test inserting, removing, and replacing SIM cards to ensure proper recognition and functionality. |
| Caller ID Test | Test the accurate display of caller information during incoming calls. |
| Network Congestion Test | Test device performance and call quality during peak usage hours. |
| App-based Services Test | Test the functionality and usability of telecom-related apps. |
| Phone Compatibility Test | Test the device’s support for telecom services and features offered by the provider. |
Popular Telecom Testing Tools
| Tool Name | Description | What it does |
| Wireshark | A network protocol analyzer for packet-level inspection. | Wireshark captures and analyzes network traffic, making it crucial for diagnosing and troubleshooting network issues. It can decode various protocols and provides real-time monitoring. |
| Spirent TestCenter | A comprehensive network testing and analysis solution. | Spirent TestCenter conducts extensive testing of network equipment and services, including traffic generation, network emulation, and performance testing. |
| Ixia | A platform for network and application testing. | Ixia offers testing solutions for network performance, security, and application testing by simulating real-world traffic conditions to identify potential issues and vulnerabilities. |
| Hammer Call Analyzer | A tool for voice quality and call performance analysis. | Hammer Call Analyzer evaluates voice quality, call setup, and performance for VoIP and telecom networks, helping to identify and resolve voice-related issues and improve call quality. |
| SIPp | A testing tool for SIP protocol-based VoIP applications. | SIPp tests the functionality and performance of SIP-based VoIP systems by generating SIP traffic, simulating calls, and measuring call quality. |
| Netrounds | A cloud-based active network testing and monitoring solution. | Netrounds enables active testing of network services by generating synthetic traffic and measuring performance, ensuring quality of service (QoS) for telecom services. |
| BreakingPoint | A network security and performance testing platform. | BreakingPoint simulates realistic network traffic to test security infrastructure, identify vulnerabilities, and evaluate network performance under stress. |
| QualiTest | An automation platform for testing telecom systems. | QualiTest provides end-to-end testing automation solutions, ensuring efficient and reliable testing processes for telecom systems. |
| JDSU MTS | A modular test solution for telecom and fiber optics. | JDSU MTS offers a variety of modules for testing telecom networks, including fiber optics, transport networks, and wireless technologies. |